Serilog
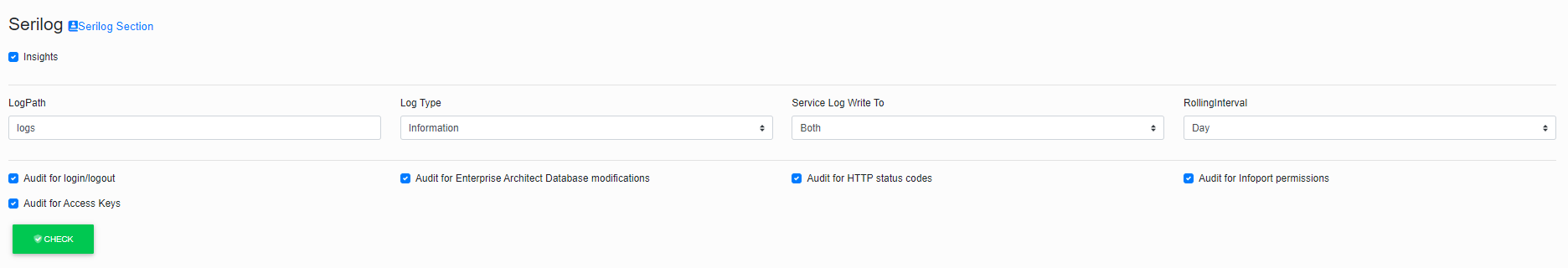
The next section allows us to set the Infoport logging.
The first item is a check box that says whether user activities should be logged. (List of visited URLs).
In the second item, we choose the relative path for saving logs.
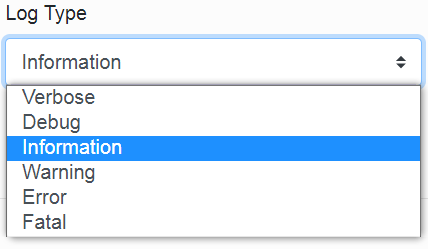
In the third item, we select the type of logging.
(Each type is described in the table. We recommend Information logging.)
Table for logging types.
|
Level (from the most detailed to the least detailed) |
Description |
|
Verbose |
For information that's typically valuable only for debugging. These messages may contain sensitive application data and so shouldn't be enabled in a production environment. Disabled by default. |
|
Debug |
For information that may be useful in development and debugging. Example: Entering method Configure with flag set to true. Enable Debug level logs in production only when troubleshooting, due to the high volume of logs. |
|
Information |
For tracking the general flow of the app. These logs typically have some long-term value. Example:Request received for path/api/todo |
|
Warning |
For abnormal or unexpected events in the app flow. These may include errors or other conditions that don´t cause the app to stop but might need to be investigadet. Handled exceptions are a common place to use the Warning log level. Example: FileNotFoundException for file quotes.txt. |
|
Error |
For errors and exceptions that cannot be handled. These messages indicate a failure in the current aktivity or operation (such as the current http request), not an app-wide failure. Example log message: Cannot insert record due to duplicate key violation. |
|
Fatal |
For failures that require immediate attention. Examples: data loss scenarios, out of disk space. |
In the fourth item, we select where we want the logs to be written. We have three options: Console, File or Both.
In the fifth item, we choose how often the log file should be closed.
Here we can see the chosen day. This means that a new log file is created for the portal every day. Logs from previous days remain on disk.
Audit for login/logout
The "/Account/Login" and "/Account/Logout" events are logged, both successful (StatusCode == 302) and unsuccessful ones.
Audit for Enterprise Architect Database modifications
Logs changes that users make to repository data. Adding, editing and deleting Packages, Element, Diagram, Attribute, Operation, etc.
Audit for HTTP status codes
Audit for Infoport permissions
Both approved and denied accesses are logged. These are always calculated for the requested Package and separately for personal and group permissions.
Warning: there may be a large number of these entries in the log.
In addition, changes to user and group permissions made by administrators are also logged. From these logs, it is possible to see who has assigned or removed what permissions when.
Audit for Access Keys
Creation or deletion of an access key is logged so that it can be determined who ever created the key, which is then used for direct access (where no explicit user logging is required)
After filling in, just press the  button and the manager will tell you if everything is OK.
button and the manager will tell you if everything is OK.



No Comments